SECS/GEM is an international SEMI standard that standardizes communication between manufacturing equipment and host systems in semiconductor industry. It enables remote control, data exchange, and alarm messages—and forms the base for the efficient integration of machines in modern semiconductor fabs.
What is the SEMI SECS/GEM standard?
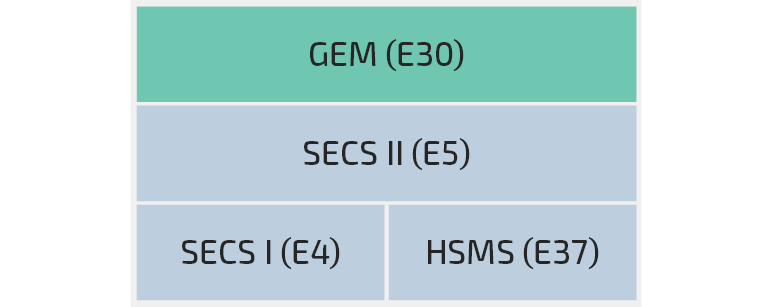
The SEMI SECS/GEM standards form the basis for efficient system integration and are a combination of several SEMI standards. They include the following SEMI standards:
- E4 – Specification for SEMI Equipment Communications Standard 1 Message Transfer (SECS-I)
- E5 – Specification for SEMI Equipment Communications Standard 2 Message Content (SECS-II)
- E30 – Specification for the Generic Model for Communications and Control of Manufacturing Equipment (GEM)
- E37 – Specification for High-Speed SECS Message Services (HSMS) Generic Services
- E167 - Specification for Equipment Energy Saving Mode Communications (EESM)
These layers ensure that data can be transferred and evaluated in a standardized manner.
- The first layer is the communication protocol. While RS-232 communication (SEMI E4 - SECS-I) used to be sufficient, it is now common to use the faster TCP/IP connection (SEMI E37 - HSMS).
- The second layer, SEMI E5 - SECS-II, describes the structure and content of the messages to be transmitted. These messages, referred to as “functions,” are grouped into “streams” according to their purpose (e.g., job management).
- The third layer is the General Equipment Models (GEM). It provides the fab host with information and describes the expected behavior and capabilities of the equipment and the host/MES (SEMI E30). This includes, for example: remote control, output of data, alarms, and events, process program management (PPM), and state models.
What role does SECS/GEM play in the semiconductor manufacturing process?
The SECS/GEM standard plays a key role in semiconductor manufacturing worldwide. It provides a standardized interface that allows equipment and host systems to communicate with each other uniformly, regardless of the manufacturer. This reduces integration costs and enables faster production readiness in semiconductor factories.
In addition, SECS/GEM enables a high degree of automation. Functions such as remote control, continuous data logging, and reliable process monitoring ensure that production processes can be controlled and monitored more efficiently.
SECS/GEM forms the base for advanced standards such as GEM300, which are indispensable in modern, fully automated semiconductor fabs. SECS/GEM thus forms the basis for integration into a future-proof production environment.
What are the advantages of using SECS/GEM for OEMs and semiconductor factory operators?
The SECS/GEM standard offers decisive advantages for semiconductor manufacturing. It enables faster integration of new equipment into existing production environments, thereby reducing commissioning costs. At the same time, the interface allows for easy expansion with additional functions, so that equipment can be flexibly adapted to new requirements. SECS/GEM also contributes to improved productivity: processes can be controlled more efficiently, downtime is minimized, and idle times are significantly reduced.
As an internationally accepted interface, SECS/GEM is established worldwide at fabs and OEMs and forms the base for market entry and sustainable competitiveness in the semiconductor industry.
How does FabLink® support the implementation of SECS/GEM for equipment manufacturer and semiconductor factory operators?
Our SEMI interface solution, FabLink® interface software, supports the implementation of all relevant SECS/GEM standards and ensures that systems can be quickly and reliably integrated into existing production environments. FabLink® meets the requirements of fabs and OEMs in the global semiconductor market. Additional SEMI standards can be implemented on an individual base.
The integration of FabLink® offers clear advantages: short project durations and predictability thanks to calculable costs, fast commissioning with minimal downtime, and the configuration of follow-up projects, which can be carried out independently and directly by the OEM.
In addition to SECS/GEM, FabLink® offers solutions for GEM300 and EDA (Interface A).
Would you like to find out more about how you can implement the SEMI standards for your equipment? Send us a message directly and we will get in touch with you as soon as possible.
FAQs: SEMI Standards – SECS/GEM
SECS/GEM is an international SEMI standard for communication between manufacturing equipment and the factory (host system). It combines two parts: SECS (SEMI Equipment Communication Standard), which defines the message formats and transmission protocols, and GEM (Generic Equipment Model), which describes the basic functions and behaviors of the machines and systems. SECS/GEM thus enables standardized functions such as data collection, alarm and event messages, and the sending of remote commands. SECS/GEM is used particularly in the semiconductor industry to seamlessly integrate equipment from different manufacturers into a higher-level production control system. The advantages lie in interoperability, simplified integration, and the possibility of automated process control and quality monitoring.
SECS/GEM is implemented by establishing standardized communication between production equipment and the factory (host). The SECS protocols (SECS-I via RS232 or HSMS via TCP/IP) define message transmission, while GEM (Generic Equipment Model) specifies which functions are supported, such as alarm messages, status reports, or remote commands. In practice, an SECS/GEM stack is integrated into the control system on the equipment side, which processes messages in accordance with SEMI standards (SEMI E4, E5, E30). The host uses middleware or specialized software to evaluate data, send commands, and control processes. Tests with simulators ensure that all GEM scenarios are mapped in accordance with the rules. In practice, a GEM300 stack (software library or toolkit) such as Fablink® from Kontron AIS is often used, as in-house development is often costly and complex.
SECS is a family of standards for communication between host and equipment with the aim of exchanging messages, commands, and data via a uniform protocol.
There are two levels:
- SECS-I (SEMI E4): Communication via serial interfaces (RS-232/RS-485).SEMI E37 is the more modern version and enables faster communication via HSMS / TCP/IP.
- SECS-II (SEMI E5): Defines the structure and format of messages (e.g., S1F1 = status request).
GEM is a functional standard (features that a system must have in order to be “FAB-compatible”). GEM is a functional model based on SECS-II of the SECS standard and ensures that all machines and systems in a fab can be controlled and monitored consistently.
SECS/GEM is the “nervous system of semiconductor manufacturing.” It connects machines and factory control systems, enables automation, ensures quality, and makes global standardization possible. Without SECS/GEM, every factory would have to develop individual interfaces for each tool, which would be expensive and prone to errors.
With SECS/GEM, equipment manufacturers can deliver their machines directly “FAB-ready.” This saves effort into integration and speeds up the commissioning of new systems. Modern semiconductor factories (e.g., Infineon, TSMC, Intel) operate with a very high degree of automation. Carriers and FOUPs with wafers often move from tool to tool without human intervention. This requires reliable equipment communication:
• Starting/stopping jobs
• Loading recipes
• Status messages
• Error/alarm handling
This is exactly what SECS/GEM delivers.
SECS/GEM and GEM300 differ in their scope of application. SECS/GEM forms the basis: it defines standardized communication between host and equipment as well as basic functions such as alarms, events, and remote commands. GEM300, on the other hand, builds on SECS/GEM and extends it specifically for 300 mm semiconductor manufacturing. It describes additional standards (e.g., for cassette handling, wafer tracking, job management) and ensures that complex material transport and process steps in highly automated factories run consistently. While SECS/GEM provides the general communication layer, GEM300 delivers industry-specific specifications to enable the complete automation of 300 mm production lines.
SECS/GEM uses standardized interfaces to ensure communication between the host system and equipment. There are two variants at the physical level: SECS-I (SEMI E4), which uses a serial RS-232 connection, and HSMS (High-Speed SECS Message Services, SEMI E37), which is based on TCP/IP and is common in modern factories. In addition, SECS-II (SEMI E5) defines the message structures that are transmitted via these interfaces. This enables commands, status messages, alarms, and process data to be exchanged reliably. Together, these interfaces form the base on which GEM (SEMI E30) provides standardized functions for monitoring, control, and data collection.
SECS/GEM is primarily used in highly automated manufacturing environments, particularly in the semiconductor industry. There, it serves as the standard for communication between production equipment and factory automation. Typical applications include wafer manufacturing, lithography, etching, and measuring equipment, where host systems monitor machine status, collect process data, and send remote commands. SECS/GEM is also used in related industries such as photovoltaics, LED, and display manufacturing, as a uniform interface facilitates the integration of equipment from different manufacturers. Its use enables end-to-end automation, higher process reliability, fewer manual interventions, and better quality assurance in complex production lines.





